Still stuck on a one-product offering? Why it’s time to adopt a new multi-product ecosystem
Are you still stuck on a one-product offering? Find out why it’s time to adopt a new multi-product ecosystem – and the best one to choose.
Julia Chanteray has spent hundreds of hours reading, researching and reverse engineering products businesses to discover the secrets of their success. And after working with dozens of clients who have successfully ‘productised’ what they do, she has distilled her findings into an exciting new ecosystem approach.
Ion this article she guides you through the easy-to-follow process, which will super-boost your earnings potential and see your business swiftly flourish.
The approach in a nutshell
You need a product ecosystem. What is a product ecosystem? Essentially, it’s a group of products that work together. They’re all related to some degree, but they’re different in how they serve your customers.
Whether you’re concentrating on productised services, stand-alone products or a mix of the two, having multiple offerings in the same ecosystem makes sense.
Into the forest: how does your product ecosystem grow?
A forest isn’t just an assortment of trees: it’s all kinds of organisms working together in a natural ecosystem. Your product ecosystem is similar. Maybe a grand old oak tree in the centre with beech trees around it.
Underground, a vast network of fungi shares nutrients with the trees. Squirrels live in the trees and eat their seeds, stag beetles burrow into the leaves shed by the trees, bats live in the holes in the older trees pecked out by woodpeckers, and all these animals provide nutrients for the trees in return. Each part is independent, but they all work together and support each other.
Your products are like this forest. Each can be appreciated (and purchased) in its own right, and they work better together, reinforcing the whole system. One product creates the right conditions for someone to buy another and they’re all part of your online presence, website and other channels, like the emails you send to people who sign up to get your first products – your lead magnets. I’ll explain more about this further down.
Explore the bigger business picture at the get-go
Your product ecosystem means you can help clients at the right level, and planning the components of your ecosystem from the beginning averts the classic mistake of trying to build your signature product first. With an ecosystem mindset, you can make your products in a modular fashion and:
- Reuse your content in different formats
- Add extra parts for the more complex products
- Cut sections out and simplify them for use in the less expensive products.
You can easily create a simple, low-cost product in a particular area to test its potential and see if anyone is interested before investing lots of time and energy in something more extensive.
And most of all, developing your product ecosystem hugely increases your customer lifetime value. Several different products make your customers more likely to repeatedly buy from you, making you more money and increasing the long-term prospects for your business. It’s a win-win!
The different kinds of products in an ecosystem

You can see your products along a line of increasing size, complexity and price, and divide them into different types such as:
- Lead magnets – useful freebies to start engaging with new potential people.
- Tripwires – low-priced tools and guides where people will often make their first purchase from you, knowing that they can check you out for a small, virtually risk-free sum.
- Medium-sized products – usually the ones you want to sell the most of.
- Big products and premium products – a crucial part of your pricing.
Dividing your products this way gets you started, but it’s not in itself an ecosystem. It doesn’t show the relationship between the products, and it doesn’t help us think about them from the customers’ point of view – the essential people in this relationship.
How to bring your secret sauce to the table
All of the products in your ecosystem need to be related to one another through:
- Your “magic”– the secret sauce behind how you uniquely help your clients. It might be a methodology you’ve come up with over the years, an aspect of your in-depth knowledge or a unique way of seeing what you do.
- All the products are for roughly the same group of people (with varying budgets), who all have a particular problem you can solve for them through your products.
Product ladders and value ladders
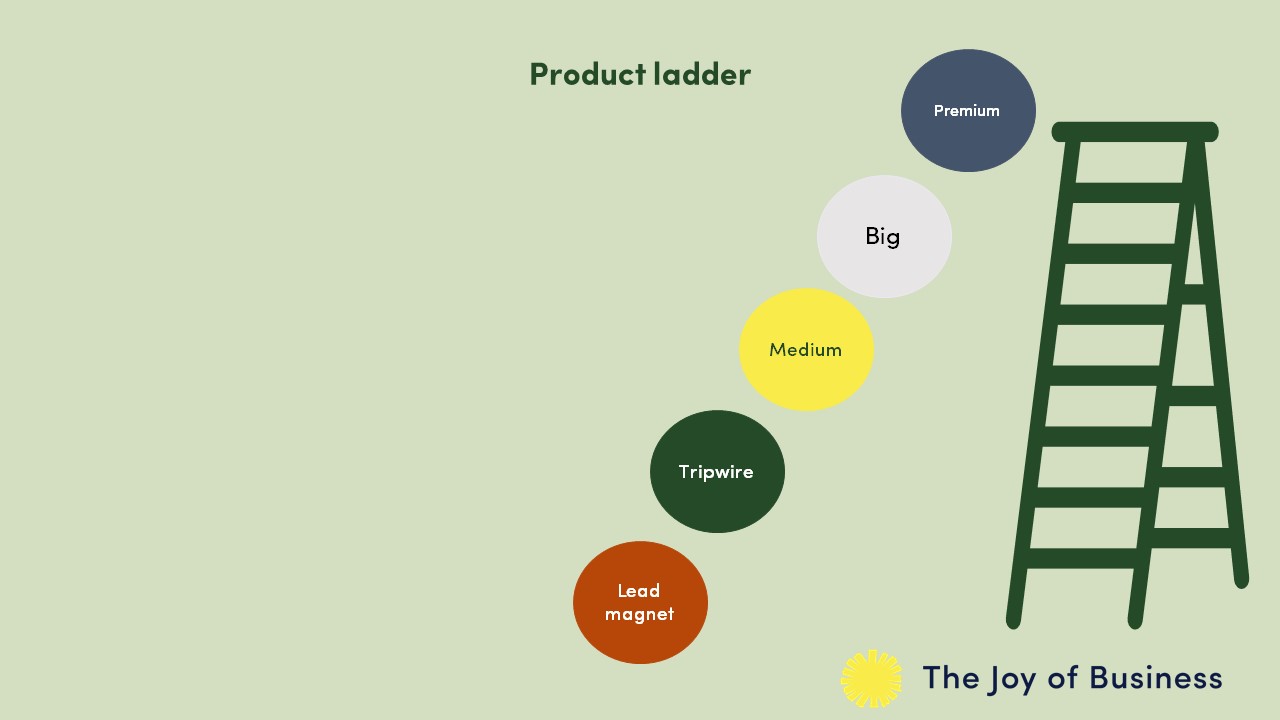
You might have come across the idea of the product ladder or value ladder. I have some reservations about this approach, as you’ll see in a moment, but it can be helpful. We can see how a customer might go up the value ladder, first checking you out through some of your free or low-value products – the lead magnets and tripwires they find helpful – then buying something more substantial in the future.
But, as we know, humans behave in all kinds of ways. I’ve bought $1,500 courses just because I needed to learn certain things and I’d had a timely email from someone saying, “Hey, we’ve got this cool course.” I didn’t buy a certain number of smaller products first, working my way up the ladder, I just went for what I needed.
The crucial factor for someone buying a medium or big product is trust. Do they trust you to solve their problem?
Trust doesn’t just come when customers experience your products at the bottom of the value ladder. Every possible interaction with your potential customers needs to be about building on their trust in you.
I see people who have never bought from me before going straight for a premium product and spending 10k. Sometimes, this is their first visit to my website; they’re not even on my email list. Through my website content alone, I’ve been able to give them a sense that they can trust me.
When it comes to selling premium products, I have further reservations about the value ladder. When you charge more than 5k for something, you can’t just depend on your ladder to build the necessary trust. You probably need that extra bit of trust-building that comes from enabling them to meet you, at least on Zoom.
The linear value ladder approach is too simplistic and can lead you astray. I believe it’s much more helpful to get your head around the alternative idea of having a product ecosystem.
The three types of product ecosystems explained
The product ecosystem approach gives you a much more nuanced and flexible way of working out what kinds of products you want to make. And how you can encourage people to buy more than one – and buy the ones that will earn you the good money.
Let’s take a look at some of the possible product ecosystems you might use.
1) Your basic product ecosystem

This example is fairly typical. You’ve got a bunch of lead magnets to draw traffic to you and encourage people to permit you to start sending them emails. Then you have some tripwire products to generate a pleasant background hum of tiny Stripe payment notifications, bringing you small amounts of cash.
Then there are a few medium products and maybe a bigger one and a premium one. You can see how this is much more nuanced and flexible than the value ladder idea.
Don’t worry if you look at this and think, “Gosh, Julia, how many products do you think I can make?” You don’t need all of them to start. Begin with a couple of lead magnets – but with the ecosystem image in mind.
Concentrating on the lead magnets and tripwire products first, before you tackle the more extensive products, enables you to start building your audience, your tribe of fans. And it allows you to develop your thinking about your specialist area – which can be delightfully challenging at the same time.
Your ecosystem is not just the products themselves. When someone grabs a lead magnet, they’re giving the thumbs up for you to send them more helpful insights, so you can regularly send emails shot through with your brand personality.
You can open a dialogue with them about how you solve that central problem for clients. And maybe send a smattering of invitations for them to engage with you through surveys, quizzes or just by hitting reply. That builds trust, so when you’re ready to promote your pricier products, most of your tribe are happy to buy them.
2) An ecosystem for an audience with smaller budgets

You’ll see that this product ecosystem has many more tripwire products and no premium. You could easily make a good living from this – a collection of low-priced tripwires and one medium product. I’ve reverse engineered many of the brands that work this way to learn from them.
This setup can be an excellent place to start because all the time you’re selling those tripwire products, you’re building your relationships with your tribe through your follow-up emails.
3) My favourite – the recurring income ecosystem
The recurring income product ecosystem has a few lead magnets to draw people in and maybe a tripwire or two to encourage initial purchases. But the primary offering is a membership or subscription with a monthly fee. This fee might be for continued access to a library of resources or a new piece of content your members get every month.

The fee might be monthly or annual. You probably already have subscriptions to Software as a Service products like this if you’re hosting your video with Vimeo, keeping your books with Xero accounting or enjoying your snacks by post every month from Graze.
You can see why I love this product ecosystem so much. Regular cash flow is every entrepreneur’s dream. Once you’ve brought a customer in and keep solving their problem, they automatically send you money each month.
And, of course, you can have multiple recurring income products all working together and add in some medium products to increase customer lifetime value.
Why the upsell is your secret weapon
We’ve talked about how humans don’t necessarily jump up the next rung of your value ladder. But there is one area within the ecosystem where you can encourage people to make a little jump, and that’s with upsells.
I once tried on some clothes at Hobbs and walked out with some rather beautiful but unsuitable boots as well as the new dresses I’d picked out because the salesperson brought the boots into the changing room. I’d been upsold a £200 pair of boots.
Within your ecosystem, you can work out what goes with what. If one of your medium products is a benchmarking report, you might upsell your client an annual subscription to all future reports. With a mastermind programme, you might sell a continuation of the programme for a lower monthly fee at the end of the initial programme.
When someone is in the process of buying one thing from you, they’re open to purchasing something else, either at the same time or very soon after their initial purchase. ASOS have studied this in-depth with all their millions of purchasers and discovered that people are most likely to buy again from them within six weeks of their initial purchase while basking in the feelgood glow of their positive experience with the company. If you ever buy anything from the online fashion giant, you’ll get a whole stream of emails from them in that six-week window, suggesting all kinds of other purchases.
Let’s get moving
Now the product ecosystem approach gets clever. You can add upsells and downsells (where you offer a less expensive alternative product to people who haven’t bought your medium product) and encourage people to move around the product ecosystem until they find something right for them. And encourage them to come back.
At this point, the product ecosystem starts to give you, and your customers, a lot more choices.
Get your priorities straight but be flexible
To seed your product ecosystem, I suggest starting with your initial list of product ideas, brainstorming a whole lot more and then choosing a shortlist of the ones you’re initially committing to work on.
Then start to work out how these might fit together as an ecosystem.
But just because you planned your product ecosystem to look a certain way doesn’t mean you have to stick to that plan. If a particular product in a niche area of yours becomes super popular, you might want to reframe everything to concentrate on that niche area. Maybe someone else will ask you to resell their product for them, and there’s a simple addition to your ecosystem and profits right there. Or you might come up with a fantastic new product idea six months from now and include that in your ecosystem.
These are all great ways for your product ecosystem to evolve and mature.
Channel your inner Marie Kondo
It’s worth being mindful of the way ecosystems can potentially change, especially if you’re like me and tend to stick for dear life to a plan once you’ve made it.
Be open to retiring or hiding some of your products after a couple of years. Either they don’t sell that well, they become out of date, or you prefer that people buy something else. When you’ve made a tripwire version first and then dug deeper to create a more in-depth product, you might find that the tripwire cannibalises sales for the big one, so you kill it off.
Or maybe you end up with such a massive list of products that your prospective customers are overwhelmed… and buy nothing. So, you need to make like Marie Kondo and de-clutter your ecosystem.
I can’t promise that there won’t be a few stumbles along the way. And you may sometimes feel like you can’t see the wood for the trees as you find the right path towards your own thriving product ecosystem. But remember that it’s a worthwhile endeavour because you’re ultimately learning how to be of more use to your tribe. And that, of course, is truly the holy grail of successful product sales.
Julia Chanteray is founder and mission controller of Adventures in Products, supporting people to escape the trap of trading time by creating beautiful ecosystems of products.




